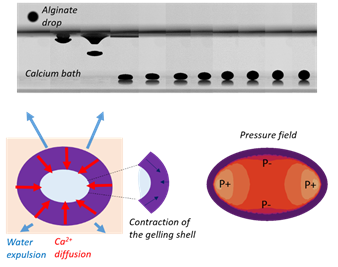
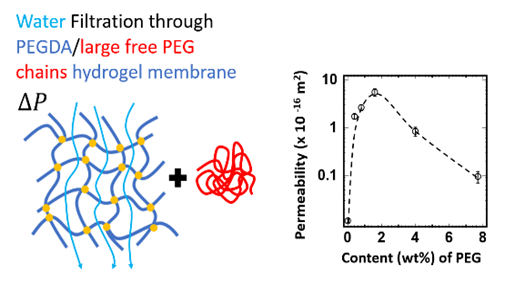
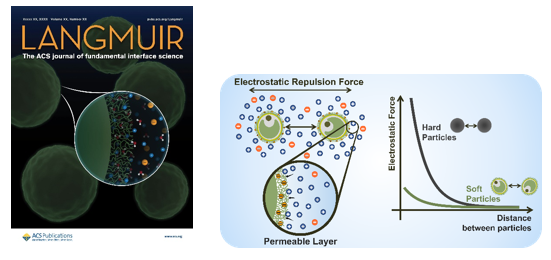
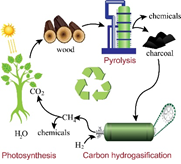
Edito
Sciences et Ingénierie de la Matière Molle - UMR7615
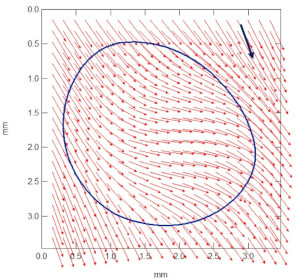
Les Sciences de la Matière Molle étudient des objets dont les propriétés macroscopiques sont fortement corrélées à leur structure mésoscopique. L’importance actuelle de cette discipline repose beaucoup sur la compréhension et l’élaboration maîtrisée d’objets aux échelles submicrométriques. Les concepts de base mûrissent depuis une quinzaine d’années, notamment sous l’impulsion de Pierre-Gilles de Gennes. Ils s’appuient sur des domaines aussi divers que la physique statistique, la mécanique, l’hydrodynamique, la physicochimie des surfaces ou la chimie. Ils irriguent maintenant des champs nouveaux comme la physique du vivant – marginale dans notre laboratoire – mais aussi un grand nombre de problématiques industrielles diverses, en particulier pour l’industrie chimique (matériaux polymères, ciments, colles, détergences…).