—Buckling driven delamination of thin films—
When low adhesion and large residual compressive stresses combine in thin films, the films may delaminate to form buckles or blisters, which often assume intriguing morphologies. We try to understand the formation of these picturesque buckles, and especially the so-called telephone cord.
 Thin film in adhesion to a substrate (in the middle section) delaminating in the form of a telephone cord (width ca 50 microns). In the side sections, the film is not adherent. As a result, the propagating telephone cord is confined to the middle of the section in adhesion with the substrate.
Thin film in adhesion to a substrate (in the middle section) delaminating in the form of a telephone cord (width ca 50 microns). In the side sections, the film is not adherent. As a result, the propagating telephone cord is confined to the middle of the section in adhesion with the substrate.
The context
Thin film mechanics is of practical significance because multilayers are ubiquitous in many tecnological areas. In many cases, residual stresses are generated during film deposition, and if adhesion is low, the film may form buckles. To prevent the formation of buckles, it is necessary to figure out why and how they form. Understanding the morphology of the blister could also lead to direct measurement of the interfacial toughness.
Our work
In the experiments, we use Mo films (molybdenum), in which we can precisely adjust the compressive residual stresses. We also developped a method to obtain a relatively reproducible film adhesion. We have studied tte size and morphology of the blisters as a function of residual stresses and film thickness.
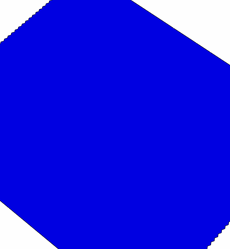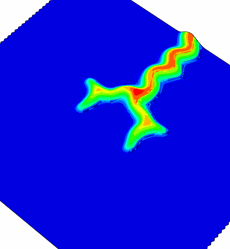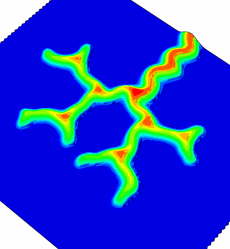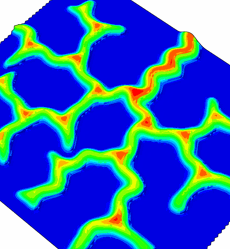 Simulations of hexagonal pattern formation by buckling. Under certain conditions, there is branching at the tip of the incipient telephone cord, leading to the formation of a hexagonal pattern.
Simulations of hexagonal pattern formation by buckling. Under certain conditions, there is branching at the tip of the incipient telephone cord, leading to the formation of a hexagonal pattern.
In order to explain the telephone cord morphology, we have carried out simulations. To reproduce the observed morphologies, we found it necessary to couple the mode mixity of the interfacial toughness (i.e mode II stronger than the mode I) to the plate non-linear elastic response of the film. This coupling has been achieved with finite elements with a cohesive zone model. Other morphologies found in the simulations are consistant with our experimental observations.
Recent Publications
– Jean-Yvon Faou, Guillaume Parry, Sergey Grachev and Etienne Barthel, "Telephone cord buckles — A relation between wavelength and adhesion", J. Mech. Phys. Solids 75 (2015) 93-103 - Journal Page, Hal
– Jean-Yvon Faou, Guillaume Parry, Sergey Grachev and Etienne Barthel, "How Does Adhesion Induce the Formation of Telephone Cord Buckles ?" Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 (2012) 116102 - Journal Page, Hal


